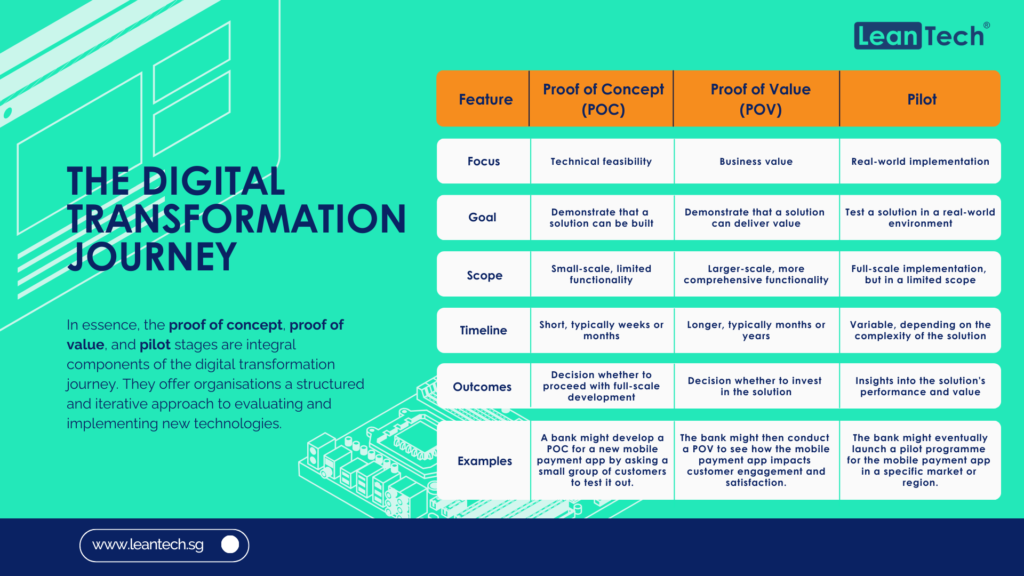
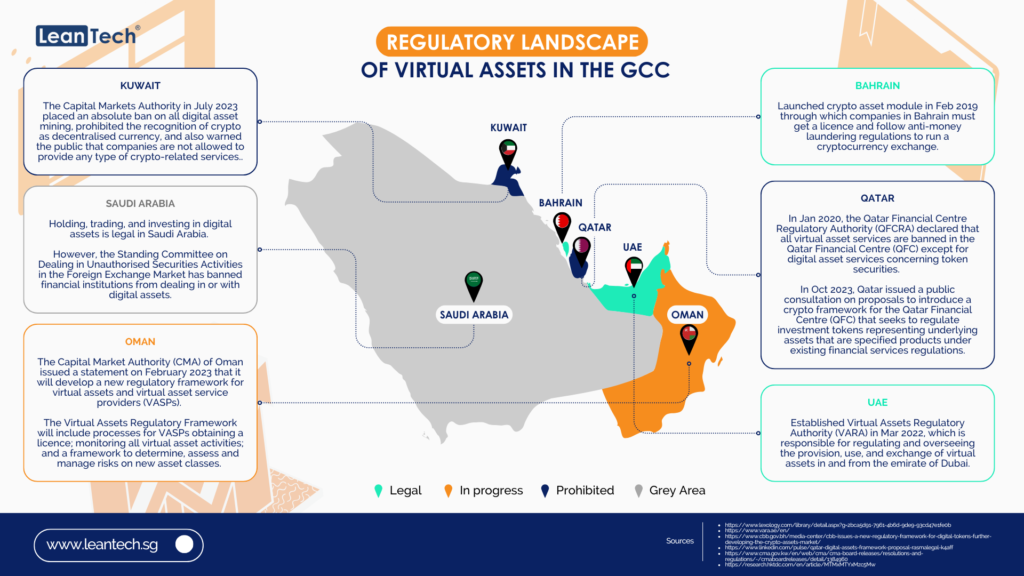
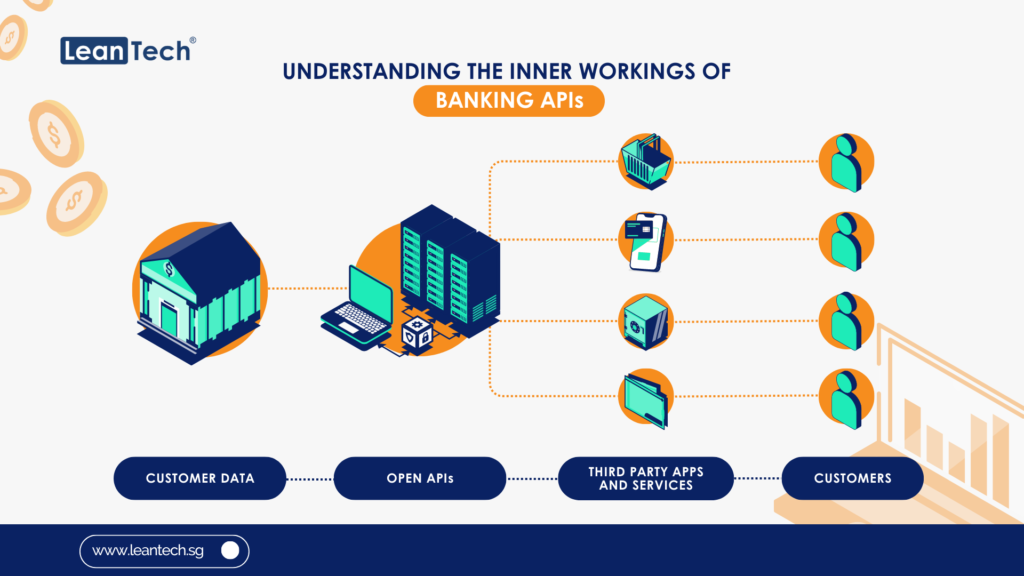
Introduction
Like every other industry, the banking and finance industry is being disrupted by new technologies. To survive and thrive, banks are harnessing cutting-edge technologies to unlock value and remain competitive. One area that is ripe for exploration is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in banking. AI can transform banks’ operations, from front-end customer service to back-end risk management.

By harnessing the power of AI in banking operations, banks can improve their efficiency, better serve their customers, reduce costs, and unlock new sources of revenue. AI can unlock $1 trillion annually in value for banks. In this article, we look at 9 leading use cases to unlock value with AI in banking and finance. These use cases belong to three major areas of AI application in banking including: improving banking processes, enhancing employees’ efficiency, and optimizing the customer experience.
Let us look into three use cases for each of these three areas of application of AI in banking operations.
AI in improving Banking Processes
New technologies are disrupting traditional business models in banking and changing customer needs and preferences. Banks are adopting AI solutions to improve processes within specific areas in the banking value chain. Here is three ways that AI is changing banking processes.
AI in Customer Onboarding
Customer onboarding involves all steps taken by banks to capture a new customer’s information, including identity checks and legal and credit-related due diligence. Slow paper-based onboarding processes record high dropout rates of clients and are costly to banks. AI allows banks to minimize client onboarding dropout rates through frictionless and remote onboarding journeys. Legacy customer onboarding takes 8-20 days, depending on compliance requirements, but AI-enabled customer onboarding takes an average of 30 minutes. AI solutions are particularly applicable in ID card verification, document verification, and biometric or face verification in e-KYC steps of the onboarding journeys. This reduced time to onboard prevented customer loss, and save operation costs for banks.
AI in Transaction Monitoring
High costs and low returns characterize legacy systems used in anti-money laundering (AML) compliance. These legacy systems often involve manually reviewing high-risk alerts, and this leads to a build-up of alert backlog. The legacy manual prioritization processes are highly inefficient and ineffective because the number of funds laundered through banks is often 9-10 times higher than what banks spend on legacy compliance and monitoring systems. AI-enabled transaction monitoring is a ‘two birds, one stone’ solution that reduces operational costs of transaction monitoring and also increases the accuracy of financial crime detection. AI-enabled monitoring and compliance processes not only increase a bank’s fraud detection capability but also reduce instances of false positives, which remain the biggest challenge to legacy systems today.
AI in Loan Processing
Legacy systems rely on credit history, credit score, and references to determine a customer’s creditworthiness. Such legacy systems are cumbersome and increase both false positives and false negatives. Eventually, legacy lending systems chip away profits and loss of customers to competitors offering seamless loan processing systems. The long processes from loan origination to disbursement, plus the paperwork and inordinate delays in verifications and approvals, lead to customer attrition. AI help resolve bottlenecks in loan processing by increasing the speed and making loan decisions more accurate and profitable. AI-enabled systems help banks to reduce loan processing times from weeks to hours and to remove profit-eating bias from loan processing decisions. The faster and safer loan processing increases profits per loan.
AI in improving Employees’ Efficiency
The back-end team of banking staff facilitates the day-to-day core banking operations, including account reconciliation, stock trading, documentation, and investment portfolio management. Legacy core banking operations are often manual and prone to errors. AI in core banking processes empowers employees to work faster and eliminate costly mistakes. Here are the three use cases on how AI improves employees’ efficiency in core banking activities.
AI in the Investment Process
Bank employees tasked with portfolio management and investment decisions often spend several days or weeks researching asset classes and each class’s respective risks before making investment decisions. Such legacy systems of investment decisions are time-consuming and prone to costly errors. AI-enable investment systems comb markets for untapped and lucrative investment opportunities and relay the results to investment bank employees to make investment decisions. The AI systems uncover additional investment opportunities that would not have been possible with human market modeling and discovery.
AI in Data Entry
Most core banking operations involve voluminous data entry tasks that are repetitive and tedious to bank employees. An employee working on legacy core banking operation tasks spends an average of 1-3 hours daily on data entry tasks alone. Such time-consuming and repetitive tasks require more dedication and commitment, and employees find it hard to stay focused; such tasks quickly demotivate employees. AI-enabled data entry systems improve data quality, enhance data validation, lead to better analytics streaming, and simplify data cleansing. AI in data entry systems saves time and money for banks and leads to happier, more engaged, and more productive employees.
AI in Collaborative Work
Core banking activities are collaborative in nature. The growth in virtual work teams has necessitated the use of collaborative technologies to improve employees’ productivity. Video calls are integral to collaborative remote working. Today, video conferencing tools have AI-enabled features like transcription, facial recognition, and even automated meeting scheduling to improve the digital collaboration experience. AI with natural language processing (NLP) can also generate employees’ insights by deciphering thousands of comments to reveal underlying concerns and apprehensions about work and help identify employees needing upskilling to boost their performance.
AI in improving Customer Experience
Digital technologies are raising customer expectations, and AI offers banks opportunities to deliver more personalization and empathy for customers. Here are the three examples of AI in banking used to deliver intelligent propositions and smarter servicing to customers.
AI in better Value Propositions
Value propositions in banking today are no longer static and one-size-fits-all. Customers’ needs are evolving, and banks can provide more personalized and situation-specific propositions to customers through real-time, AI-enabled analytics. Financials are now embedded in partner ecosystems like retailers, restaurants, and healthcare providers. Banks can offer more personalized and empathetic propositions by anticipating real-time end-to-end customer needs. AI-enabled financial management tools can inform the customer in real-time about fee reduction options while transacting with other service providers and even give them budgeting advice in their daily spending.
AI in Chatbots
Customers expect faster and round-the-clock responses to their queries and complaints. Due to time and logistical difficulties, traditional customer centers may not offer such timely and 24/7 availability. AI-enabled customer support services offer live query resolution at lesser costs, higher accuracy, and around-the-clock availability. AI chatbots in banking can assist customers with routine queries like transaction histories, account balances, payment processing, and loan processing. AI-powered chatbots today provide customers with human-like support experiences without human interventions, which helps personalize customer support and lower costs for banks. Customers can ask chatbots for queries like recent charges on their cards, report stolen cards, transfer funds, and the due dates for loan repayments.
AI in Embedded Finance
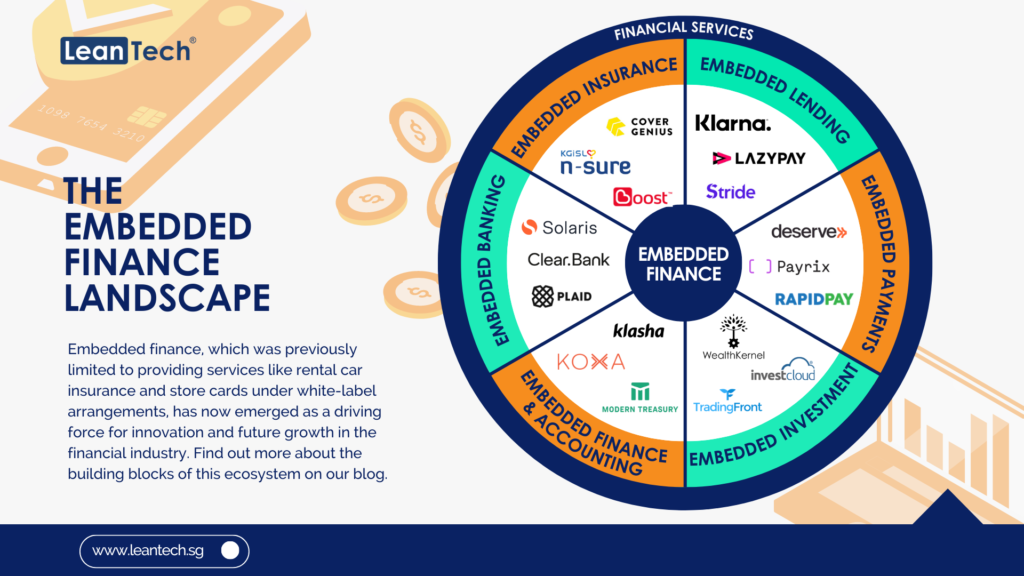
Customers want to access their money on their terms, anytime and anywhere. They do not want to go to ATMs or banking halls to withdraw cash for daily usage. AI improves the integration of payment services across non-banking platforms like e-commerce sites, transport services, and even healthcare services. AI-enabled digital apps allow customers to understand their digital ecosystems better and tap the potential of these ecosystems to create value. For example, AI solutions allow customers to pay bills and send payments within their embedded digital ecosystems with a voice command. AI-enabled embedded finance provides customers with a frictionless experience in their day-to-day transactions.
Conclusion
Businesses in all industries, including the banking and finance sector, are leveraging technologies to serve customers better and stay ahead of the competition. Advantages of AI in banking include cost reduction, operational efficiency, and better customer experience. Banks with AI capabilities have happier employees, record better revenues, and serve more satisfied customers. Most banks believe that AI is integral to achieving their strategic objectives and are planning to adopt AI to a large or very large extent in the next 3-5 years. Most banking executives are already investing in training programs to develop a digital workforce ready to deploy and benefit from AI at scale. You, too, should upskill and reskill your employees to be ready to work with AI to create value for your bank and your customers. Download our course catalog now and start your preparations for the future of AI in banking.