In the ever-evolving landscape of electronic payments, consumers worldwide are progressively shifting away from cash in favour of sophisticated digital payment methods. According to the FIS Global Payments Report 2023, digital wallets dominate both global e-commerce (ecom) and point-of-sale (POS) transactions, accounting for 49% of ecommerce payments and 32% of POS payments. In contrast, cash trails behind at 12% and 13% for these transactions, respectively. The global prevalence of digital wallets is evident, with projections indicating their continued ascendency.
Digital Wallets: The Pinnacle of Transactions
Digital wallets, also known as e-wallets, represent the fastest-growing segment among electronic payment options. Functioning as secure repositories for payment information and passwords, digital wallets streamline purchases, offer biometric authentication, and integrate seamlessly with financial institutions and merchants through open banking and APIs.
The exponential growth of e-commerce, projected at a 9% CAGR from 2022-2026 by FIS, further propels the adoption of digital wallets. Major global technology companies, including Apple, Amazon, Alibaba, Facebook, and Google, wield substantial influence, commanding over 70% of the global e-wallet market as reported by Capgemini. Leveraging expansive user bases, these tech giants prioritise delivering a seamless user experience and value-added features, capitalising on network effects. Various homegrown startups such as STCPay and Klip also entered the markets.

Types of Digital Wallets
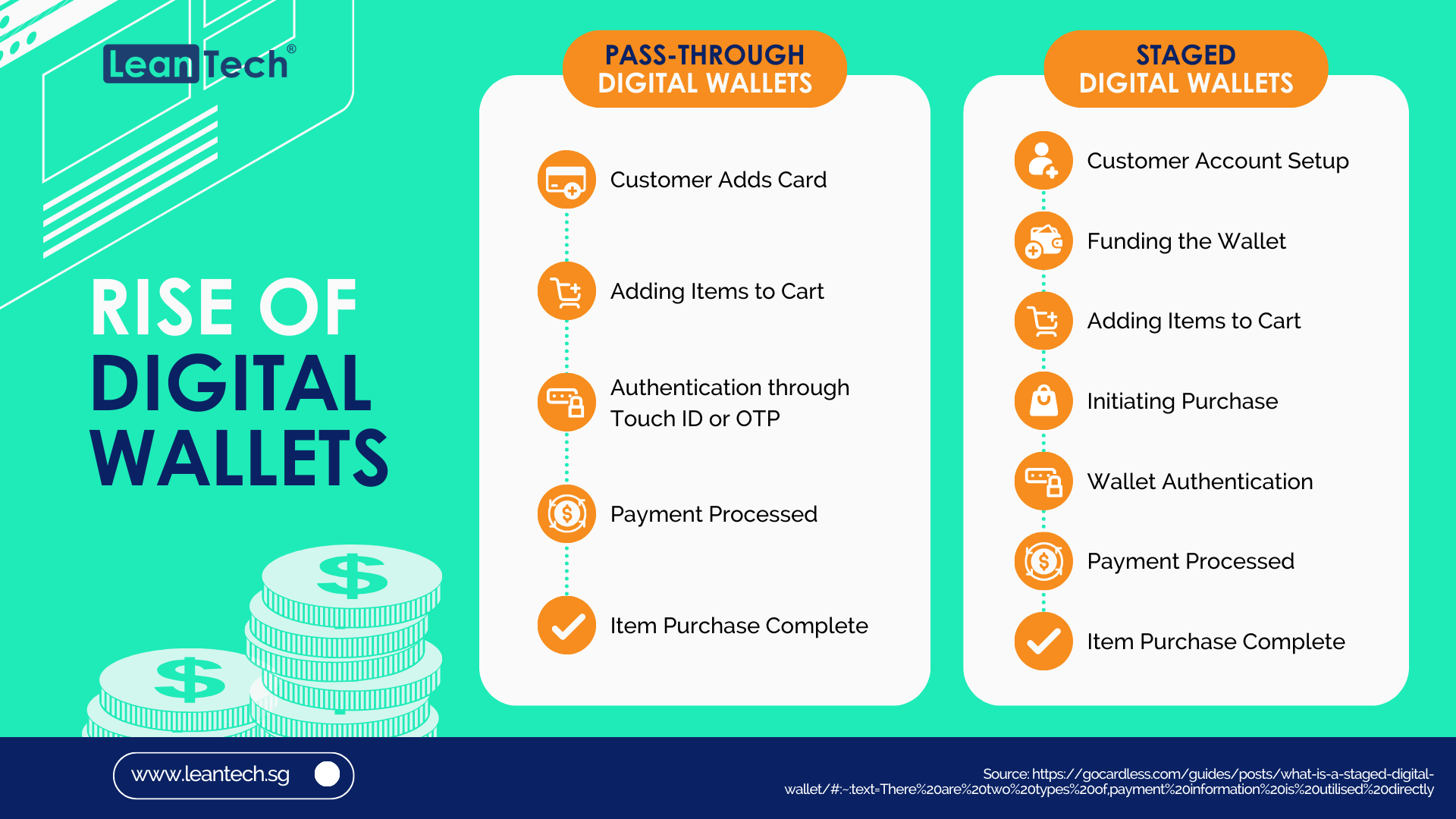
Digital wallets fall into two primary categories: pass-through and staged.
Pass-Through Digital Wallets
Pass-through digital wallets like Apple Pay, ChasePay and STCPay operate by directly utilising the card payment information, which is then transmitted to the issuer and card network. In this scenario, a physical device like a smartphone often replaces the need for a tangible debit or credit card. This is done as follows: when a user initiates a transaction, the payment information is passed through the digital wallet without the wallet itself being actively involved in the transaction. The card details are directly communicated to the card brand and issuer, facilitating a seamless and rapid payment process.
Staged Digital Wallets
Staged digital wallets, on the other hand, introduce multiple stages in the transaction process. These stages typically involve a funding stage and a payment stage, allowing the digital wallets like PayPal and Telr, to act as an intermediary between the purchaser and the merchant. To elaborate a bit:
Funding Stage: In the initial stage, the digital wallet acquires funds from the purchaser. This could involve loading the wallet with a specific amount of money from the user’s linked bank account or credit card.
Payment Stage: Subsequently, in the payment stage, the digital wallet operator transfers the funds to the business or merchant where the purchase is being made. Importantly, the card issuer and network may not be aware of specific transaction details, such as the type of card used.
Future Projections and Considerations
Digital wallets are projected to grow at a 15% CAGR at POS from 2022-2026, while cash’s share of global POS transaction value is anticipated to drop below 10%. Merchants, contemplating the use of staged or pass-through digital wallets, must carefully consider transaction fees and user preferences, ultimately aiming to provide a diverse range of payment options to meet evolving consumer needs.