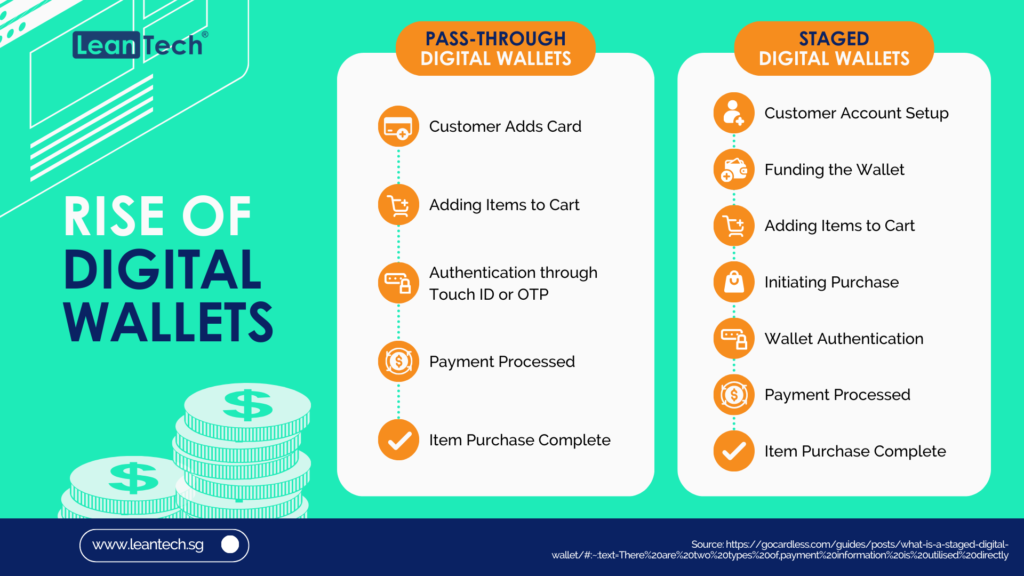
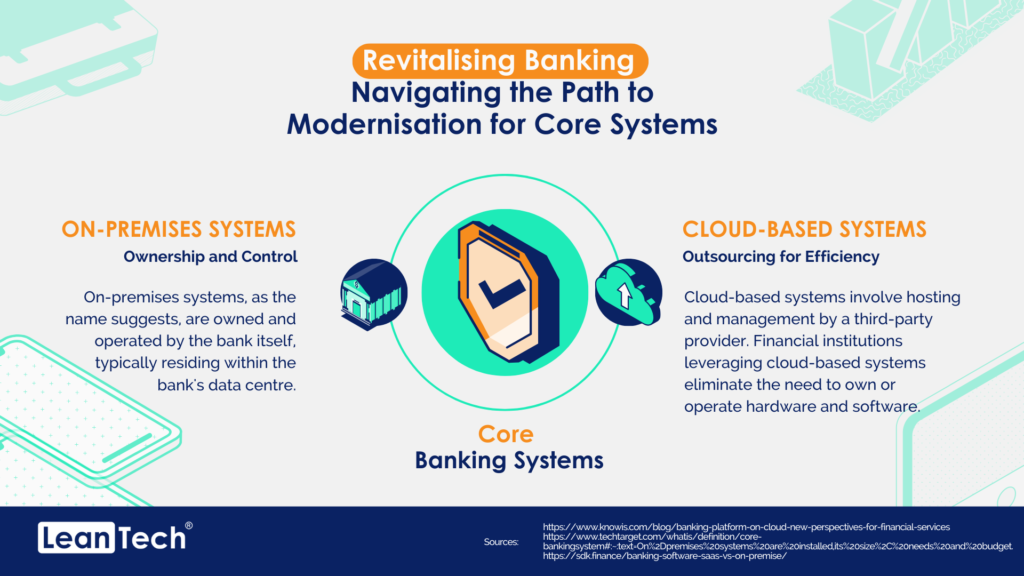
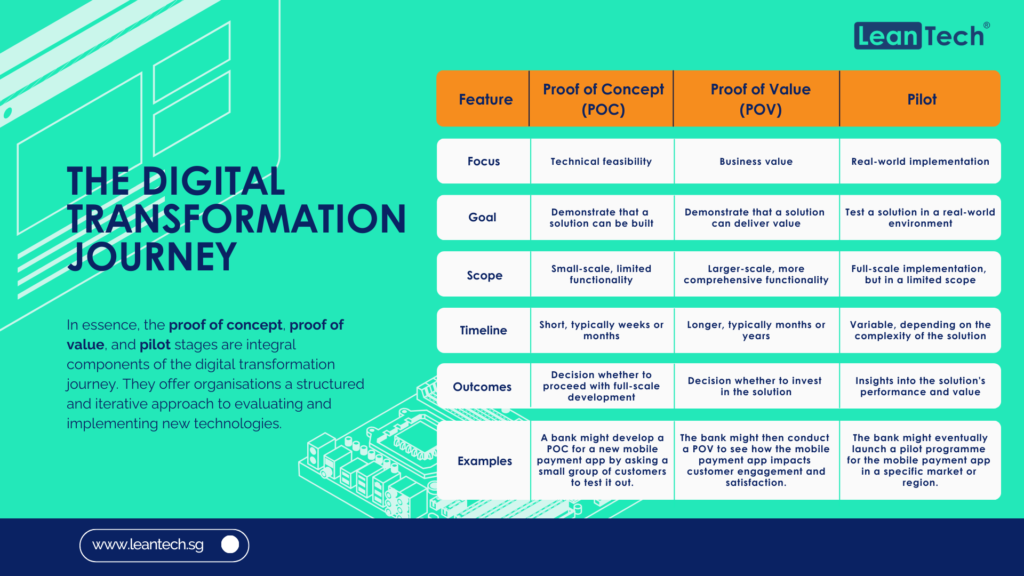
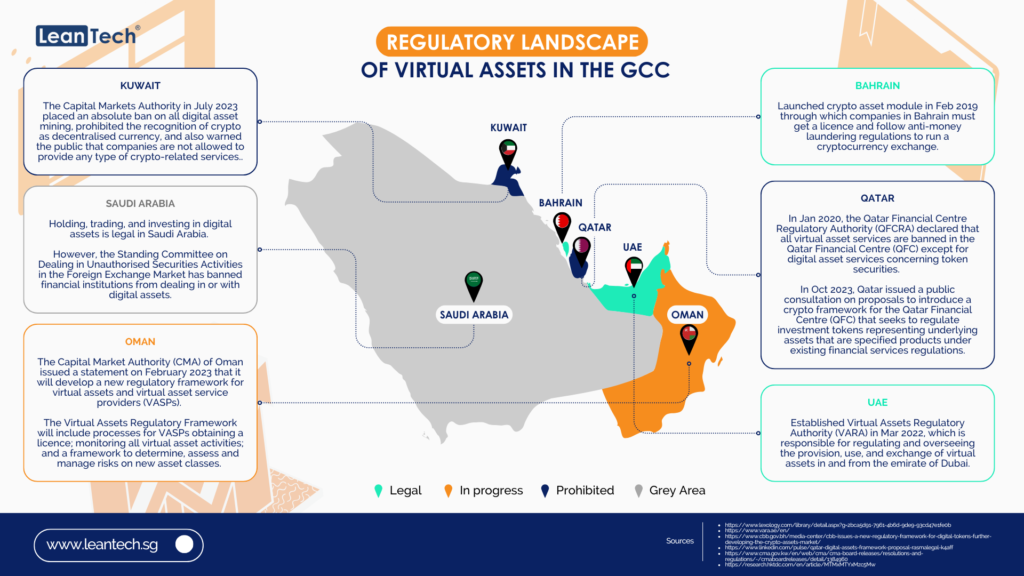
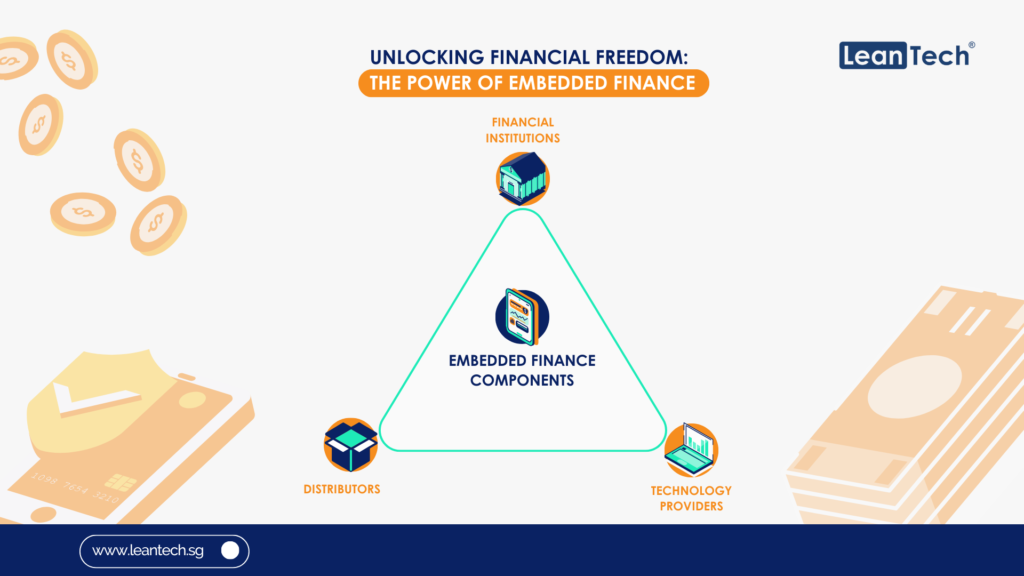
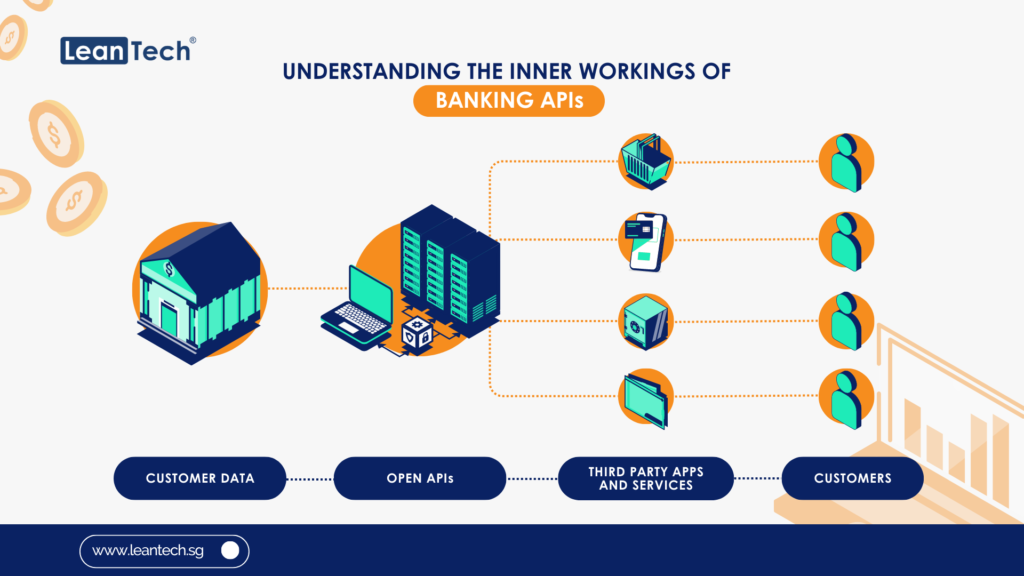
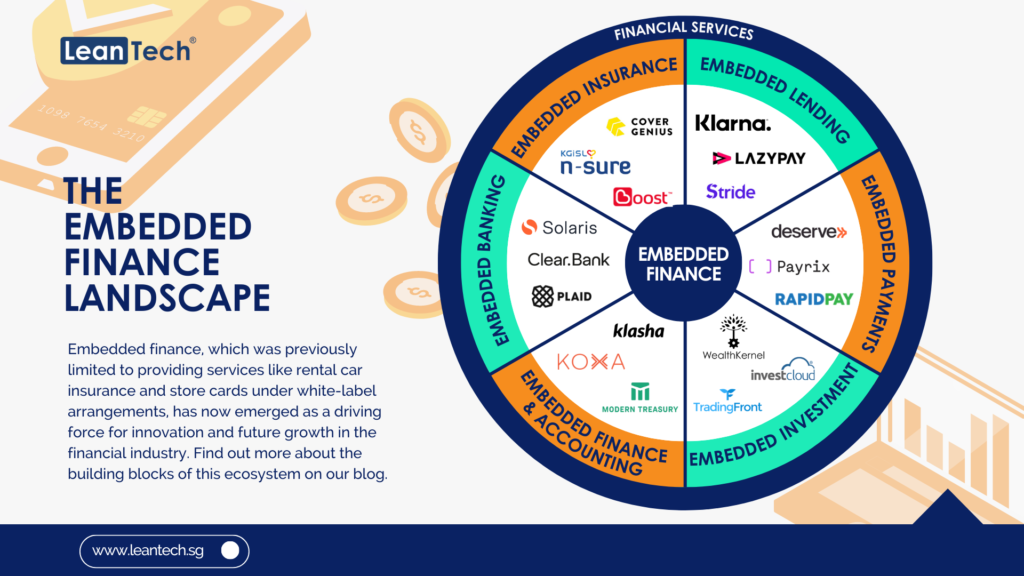
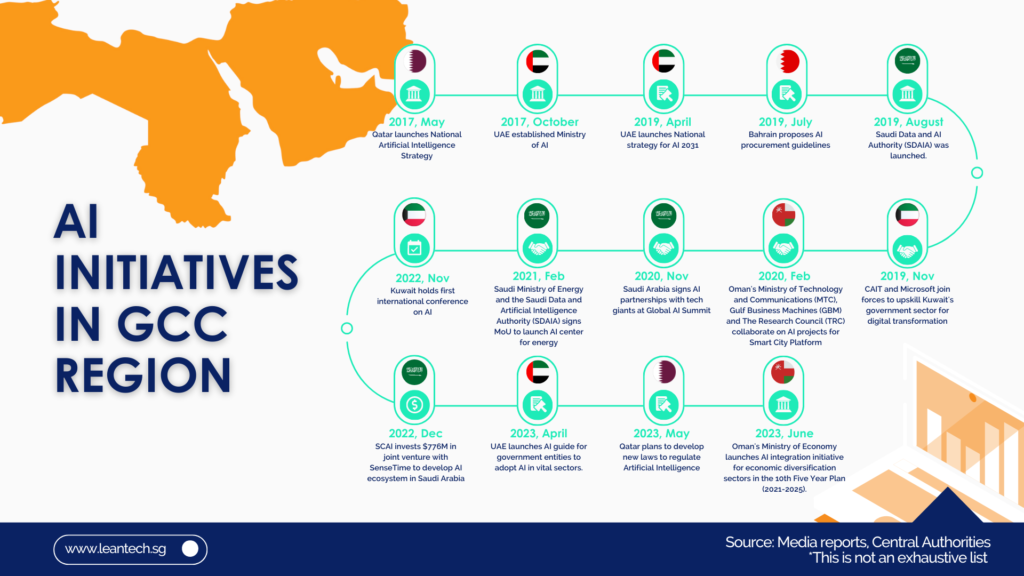
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, staying ahead of the curve is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. The financial sector is no exception, with Open Banking emerging as a transformative force that has revolutionised the way we access and manage our financial data. But as technology continues to advance, a new concept has emerged: Open Finance. And now, the latest buzzword on everyone’s lips is Open Data. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of this transition from Open Banking to Open Finance to Open Data, exploring the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead.
Understanding Open Banking
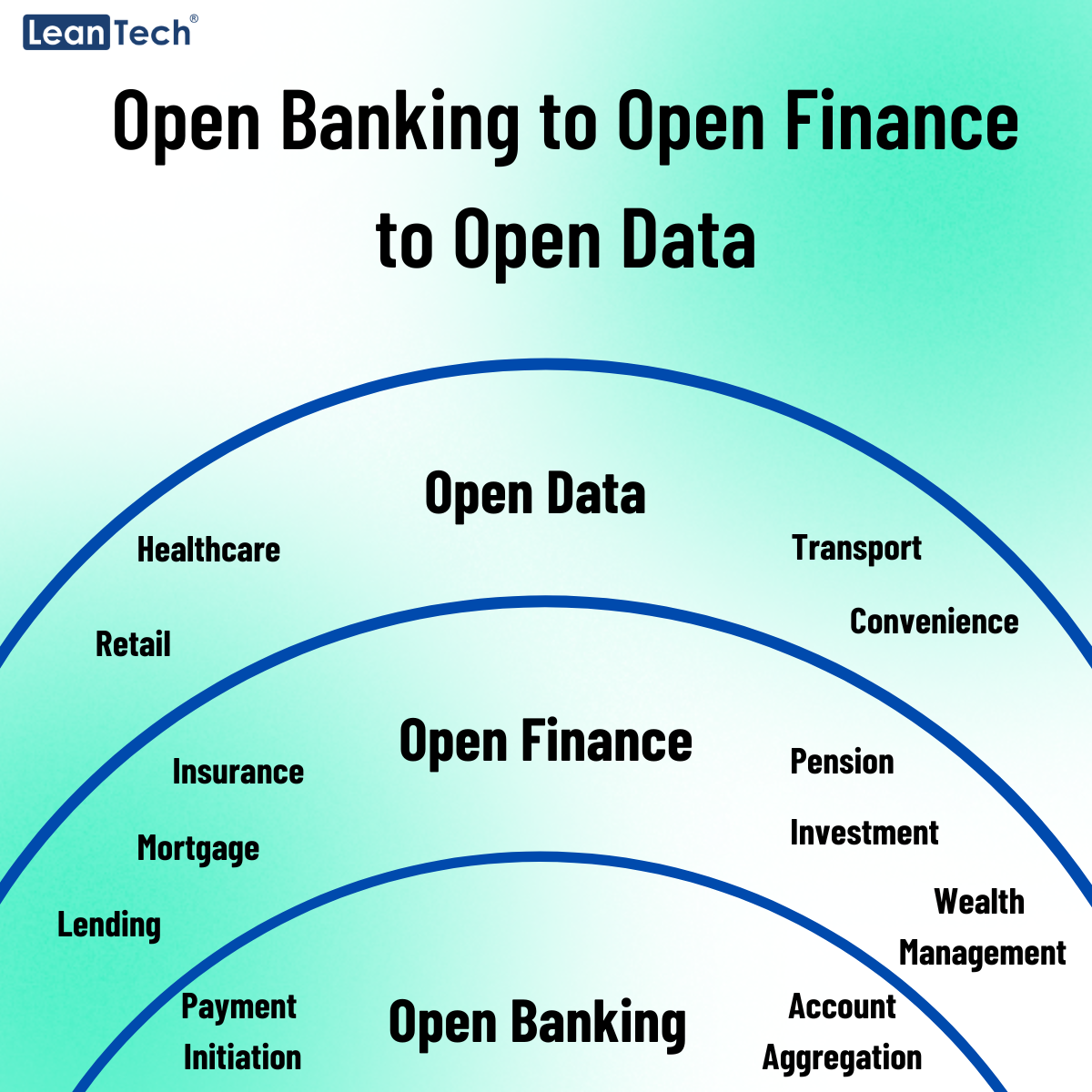
Let’s start by establishing a foundation of understanding about Open Banking. Essentially, Open Banking is a regulatory framework that enables individuals and businesses to securely share their financial information with authorised third-party providers through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). This allows for the development of innovative financial products and services that can enhance customer experiences and foster competition within the industry.
With Open Banking, customers have greater control over their financial data, enabling them to seamlessly share information between different financial institutions. This fosters a more collaborative and customer-centric approach, as it empowers individuals to access a wider range of services and make more informed financial decisions.
The Evolution to Open Finance
Building upon the principles of Open Banking, Open Finance takes a more holistic approach by extending the concept beyond traditional banking services. Open Finance aims to encompass a broader spectrum of financial products and services, including insurance, investments, pensions, and more. By embracing Open Finance, individuals will have a comprehensive view of their financial life, enabling them to make more informed decisions and unlock new opportunities.
The transition from Open Banking to Open Finance introduces new challenges and considerations. Interoperability and standardisation become crucial to ensure seamless data sharing across various sectors within the financial ecosystem. Additionally, addressing privacy and security concerns is paramount to maintain trust and protect sensitive financial information.
Open finance is also gaining traction in the GCC countries, with several countries in the region having already launched or announced plans to launch open banking frameworks.
Saudi Arabia was the first GCC country to launch open banking, in January 2021. The Saudi Central Bank, previously known as Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA), has set ambitious goals for open banking, with the aim of increasing financial inclusion, driving innovation, and improving customer experience. While, the United Arab Emirates is also planning to launch open banking in 2023, UAE Central Bank has published a consultation paper on open banking, which sets out the regulator’s vision for the development of the open finance ecosystem in the country.
Bahrain and Oman have also expressed interest in developing open banking frameworks.
The development of open finance in the GCC region is still in its early stages, but it is a trend that is likely to continue to gain momentum in the years to come.
The Rise of Open Data
While Open Finance offers a more comprehensive view of an individual’s financial landscape, Open Data takes the concept even further. Open Data promotes the sharing and accessibility of data across industries, not just limited to the financial sector. This data-driven approach encourages collaboration and innovation, unlocking the potential for new business models and services.
By embracing Open Data, businesses can gain valuable insights, identify emerging trends, and make data-driven decisions. It also paves the way for partnerships and collaborations between organisations, driving cross-industry innovation and creating new opportunities for growth.

Navigating the Transition
Transitioning from Open Banking to Open Finance and Open Data is a complex process that requires a strategic and well-thought-out approach. To give you a broader idea of how to navigate this transition, let’s delve into each consideration in more detail:
a) Regulatory Compliance: It is essential to stay updated on the regulatory frameworks governing Open Banking, Open Finance, and Open Data in your jurisdiction. Compliance with data protection and privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), is crucial to maintain trust and avoid legal complications. Engage with regulatory bodies and industry associations to understand the requirements and ensure your operations align with the prescribed guidelines.
b) Data Security and Privacy: Protecting sensitive financial information is of paramount importance during the transition. Implementing robust security measures is critical to prevent data breaches and maintain customer trust. Encryption techniques, access controls, and regular security audits can help safeguard customer data from unauthorised access. Additionally, data anonymisation techniques can be employed to protect individual privacy while allowing for meaningful analysis and insights.
c) Interoperability and Standardisation: Collaboration and standardisation are key factors in the successful transition to Open Finance and Open Data. Engage with industry stakeholders, including financial institutions, technology providers, and regulatory bodies, to establish interoperability standards. Standardised APIs and data formats enable seamless integration and facilitate smooth data sharing between different financial institutions and service providers. This interoperability allows customers to access a wide range of financial products and services from various providers, enhancing competition and choice.
d) Customer Education and Consent: Educating customers about the benefits and risks associated with Open Finance and Open Data is crucial. Provide clear and concise information about how their data will be used, who will have access to it, and the security measures in place to protect their privacy. Obtain explicit consent from individuals before accessing and utilising their data, ensuring transparency and accountability. Empower customers to exercise control over their data, allowing them to revoke consent or make changes to their preferences at any time.
e) Innovation and Partnerships: Embracing innovation is a fundamental aspect of the transition to Open Finance and Open Data. By leveraging the vast amount of data available, businesses can develop new products, services, and business models that cater to evolving customer needs. Collaborate with fintech companies, technology providers, and other industry players to explore partnership opportunities. These collaborations can drive cross-industry innovation, create synergies, and deliver enhanced customer experiences. Foster a culture of continuous learning and experimentation to stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
The way forward
Transitioning from Open Banking to Open Finance and Open Data presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses in the financial sector. By prioritising regulatory compliance, data security, interoperability, customer education, and innovation, organisations can successfully navigate this transition and unlock the benefits of a more open and collaborative financial ecosystem. Embrace the potential of Open Finance and Open Data to drive growth, foster innovation, and provide customers with an enriched financial experience.